What is Symons Rain Gauge?
A Symons rain gauge is a type of rain gauge, known as a non-recording gauge. It is designed to measure precipitation, (specifically rainfall) by collecting it in a graduated measuring tube. The volume of water collected in the tube is then measured to determine the amount of rainfall.
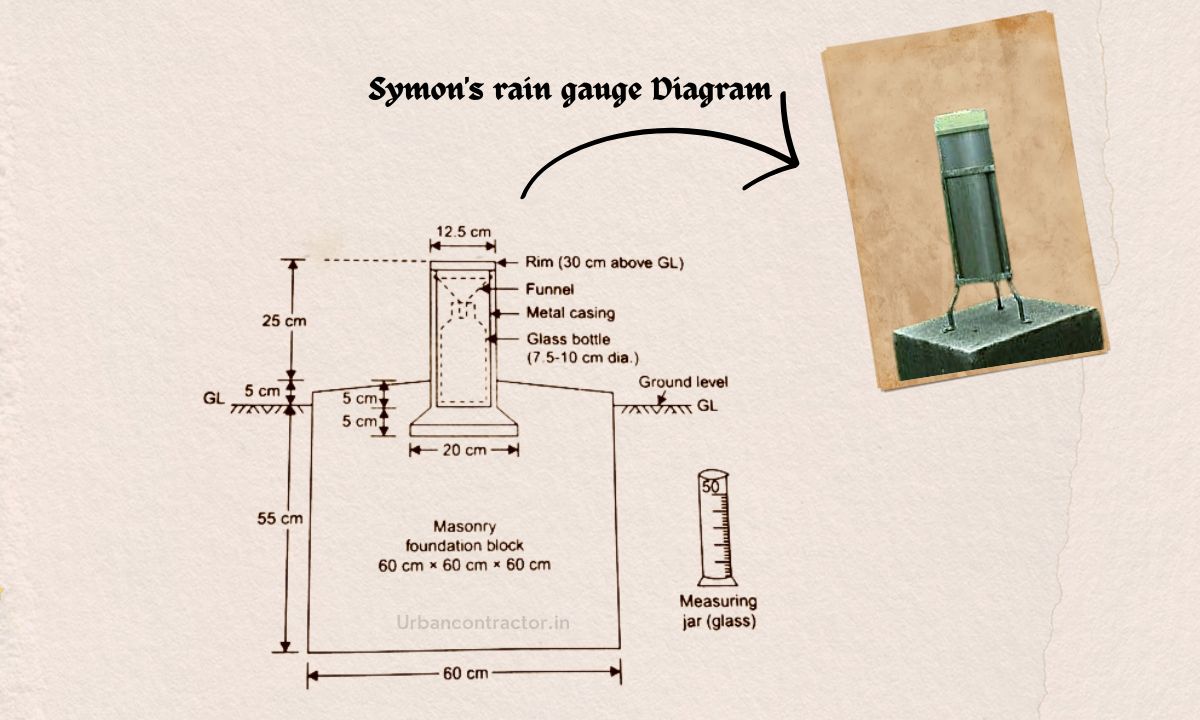
Symons Rain Gauge Diagram
The following points give a detailed explanation of the Symons rain gauge diagram:
- Funnel: Symons rain gauge has a funnel-shaped collector placed at the top to efficiently capture rainfall and direct it downward into the measuring tube.
- Measuring Tube: Below the funnel, there is a transparent or translucent graduated measuring tube. This tube is marked with calibrated measurements, typically in millimeters or inches, to indicate the volume of collected water.
- Mounting Stand: This is a stable base where the entire apparatus is mounted securely for accurate measurements.
- Overflow Mechanism: Some Symons rain gauges may feature an overflow mechanism, which allows excess water to escape without affecting the accuracy of the measurements.
- Data Collection: Meteorologists or researchers periodically check and record the water level in the measuring tube to determine the amount of rainfall accumulated over a specific period.
You might be interested in: Aggregate Test List – Types, Procedures, and IS Codes
Symons Rain Gauge Uses
The Symons rain gauge is primarily used for monitoring rainfall patterns and amounts over a specific area and period.
Symons rain gauge is commonly used in the following fields:
Weather Stations: Weather Stations use Symons rain gauges to record and analyze rainfall data, which helps them to predict weather patterns and the assessment of climatic trends.
Agriculture: The rainfall measurements data from Symons rain gauge is used in agriculture to optimize irrigation practices, manage crop water requirements, and assess drought conditions.
Hydrology: The rainfall data collected by Symons rain gauges helps hydrologists study water cycles, assess water resource availability, and analyze the impact of rainfall on river discharge and groundwater recharge.
Environmental Monitoring: The rainfall data collected by Symons rain gauges can be used to monitor the effects of rainfall on soil erosion, surface runoff, water quality, and ecosystem health.
Advantages of Symon Rain Gauge
- Symons rain gauges are cost-effective compared to some more complex rainfall measurement instruments.
- Symons rain gauges are designed with precision to accurately measure rainfall.
- Simple design and easy to use.
- Low maintenance
- Symons rain gauges are versatile and suitable for various applications, including meteorology, hydrology, agriculture, and environmental monitoring
- They can collect data for longer term.
Disadvantages of Symon Rain Gauge
- Evaporation losses can lead to miscalculations of rainfall.
- Chances of inaccuracies in measurements due to wind.
- Limited accuracy for solid precipitation like snow or hail.
- Regular maintenance is required for accurate readings.
- Spatial resolution limitations may not capture localized variations.
- Manual operation can be time-consuming.
- Susceptibility to damage from extreme weather or vandalism.
Also Read: Gully Trap – Types, Uses, Size, Importance and Chamber Diagram
FAQ’s on Symon Rain Gauge
The Symons rain gauge is also known as a non-recording type gauge, widely used in India by the meteorological department to measure rainfall.
As the name defines, Symon’s rain gauge doesn’t record rain it only collects the rain which is later measured using a graduated cylinder.