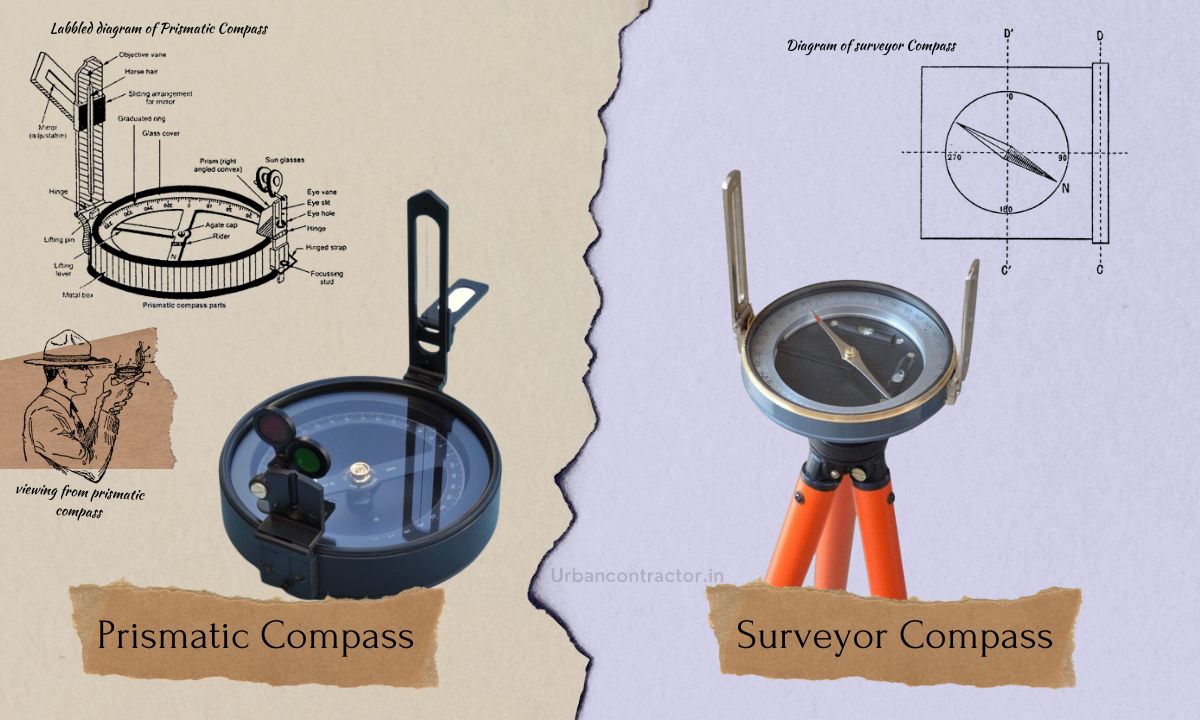
What is Prismatic Compass?
A prismatic compass is a navigational instrument consisting of a magnetic compass needle fixed within a transparent compass dial with a prism or mirror attached to it, it is used for measuring angles in the horizontal plane.
The prism/mirror allows the user to simultaneously view the magnetic compass needle and the object being sighted, facilitating angle measurement.
What is Surveyor Compass?
A surveyor compass is a precision instrument used for measuring horizontal and vertical angles in surveying and engineering applications. It is also known as a transit compass or theodolite.
The Surveyor compass consists of a magnetic compass needle, a telescope mounted on a tripod, and graduated circles for measuring angles in both horizontal and vertical planes. The telescope gives a magnified view of far objects, allowing precise angle measurements to be taken.
Also Read: Mud Floor – Ideas, Cost, Installation, Pros and Cons
Difference Between Prismatic Compass and Surveyor Compass
Following are the differences between the prismatic compass and the surveyor compass:

| Prismatic Compass | Surveyor Compass |
|---|---|
| Measures angles in the horizontal plane | Measures both horizontal and vertical angles |
| Simple, with a compass needle and prism/mirror | Complex, with a telescope, graduated circles, and leveling mechanisms. |
| Generally less accurate | Offers higher precision and accuracy |
| Primarily used for basic navigation and rough angle measurements | Used in surveying, engineering, and construction for precise angle measurement and alignment |
| Relatively easy to use | Requires training for accurate readings and adjustments |
| Generally more affordable | Typically more expensive due to precision components |
| More portable and lightweight | Bulkier due to additional components |
| Typically lacks leveling mechanisms | Includes leveling mechanisms for accuracy |
| Narrower field of view without magnification | Wider field of view with telescope magnification |
| Coarser graduations for angle measurement | Finely graduated circles for precise measurement |
| Often handheld or mounted on less stable supports | Mounted on sturdy tripods for stability |
Also Read: Aggregate Test List – Types, Procedures, and IS Codes