What is Aggregate Test in Civil Engineering?
Aggregate test is a process of performing certain tests on aggregates, as it is one of the main components of concrete. it is necessary to have certain checks for the physical properties, quality, and suitability of aggregates for specific applications in construction projects. Different types of Aggregate tests are conducted in the laboratory and field based on project requirements.
Aggregates are granular materials such as sand, gravel, crushed stone, and recycled concrete used in construction.
Why Aggregate Testing is Required?
It is very crucial to test aggregates before using them in the projects as quality, performance, safety, and compliance of aggregates, ultimately contribute to the longevity and reliability of infrastructure and built environments.
1. Quality Control: Quality on priority, Aggregate tests are conducted so the aggregates used in construction meet the specified quality standards and performance requirements. This aggregate test helps maintain the consistency of material quality, preventing the use of inferior aggregates that will affect the integrity and longevity of the structures.
2. Performance Assessment: Different projects require aggregates with specific properties such as strength, durability, and gradation. By conducting aggregate test we evaluate these properties to ensure that the aggregates will perform as expected under various conditions, such as loading, weathering, and environmental exposure.
3. Safety: Aggregate testing helps in evaluating weak or defective aggregates that could lead to structural failures or safety hazards.
4. Cost Efficiency: Using tested aggregates in projects that have passed quality standards can help minimize costly repairs, replacements, and maintenance over the lifespan of a structure.
5. Compliance: Big projects are often regulated by govt agencies which often have specific requirements for the quality and properties of aggregates used in construction. A simple aggregate test ensures compliance with these regulations and standards, preventing legal issues and project delays.
Types of Aggregate Tests in Civil Engineering
Following are the different types of aggregate tests carried out to determine various properties of aggregate.
- Crushing Test on Aggregates
- Abrasion Test on Aggregates
- Impact Test on Aggregates
- Soundness Test on Aggregates
- Shape Test on Aggregates
- Specific Gravity and Water Absorption Test on Aggregates
- Bitumen Adhesion Test on Aggregates
1. Aggregate Crushing Value Test
The crushing value test is one of the tests carried out on aggregates to determine their strength and suitability for various construction applications.
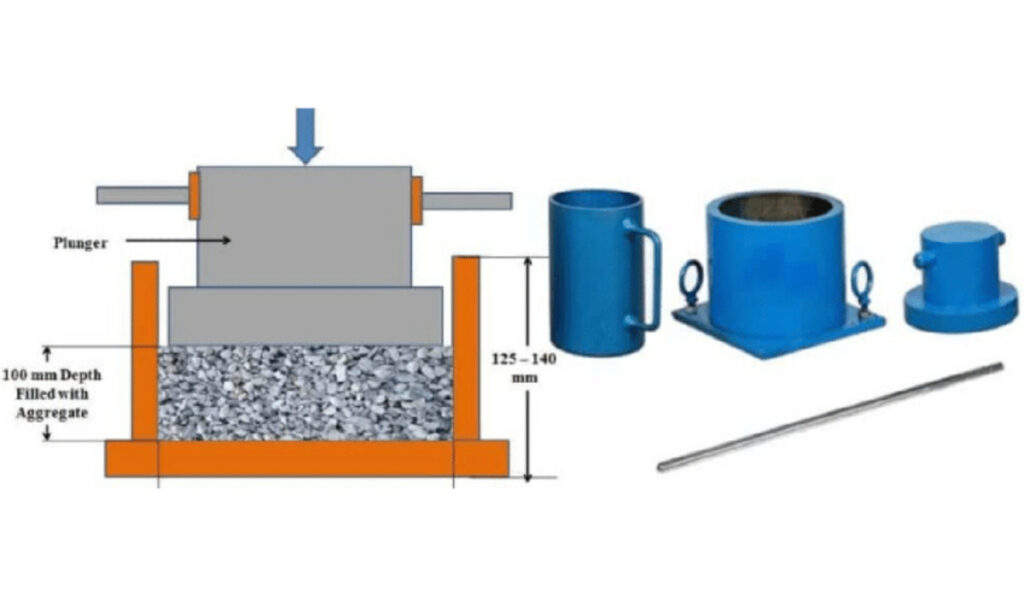
In this test, the aggregate’s resistance is determined to crushing under gradually applied compressive load.
a) IS codes for Crushing value Test:
- IS 2386(Part 4):1963
- BS 812–110:1990
b) Apparatus used for Crushing value Test:
- Compressive Testing Machine
- Crushing Mould: A steel cylinder 15 cm in diameter with a plunger and base plate.
- Weighing machine
- Sieve: Size of 12.5 mm, 10 mm and 2.36 mm
c) Procedure of Crushing value Test:
- Take some aggregate samples that are clean and free from dust and other particles.
- Now determine sample particle size distribution by using standard sieves(as per IS 2386-Part I). Record the weights retained on each sieve, and calculate the cumulative percentage passing for each sieve size.
- Now, the aggregate sample is filled in a cylindrical steel container of the aggregate crushing value apparatus in three layers, each layer being subjected to 25 strokes using the tamping rod. Level the surface.
- Now apply a gradually increasing compressive load at a uniform rate of 4 tonnes per minute until the total load is 40 tonnes or more.
- The crushed aggregate sample is then sieved through 2.36mm (IS sieve size). The weight of aggregate passing (W2)is expressed as a percentage of the weight of the total sample (W1) which is the aggregate crushing value.
d) Formula of Aggregate Crushing Value Test :
Aggregate crushing value = (W1/W2)*100
e) Results Values: Any value less than 10 is considered a strong aggregate, while a value above 35 would normally be termed a weak aggregate.
2. Abrasion Aggregates Test
An abrasion test is carried out on aggregates to determine the resistance of aggregates to abrasion and impact, which is useful to determine their durability and suitability for use in road construction and other applications subjected to wear and tear.
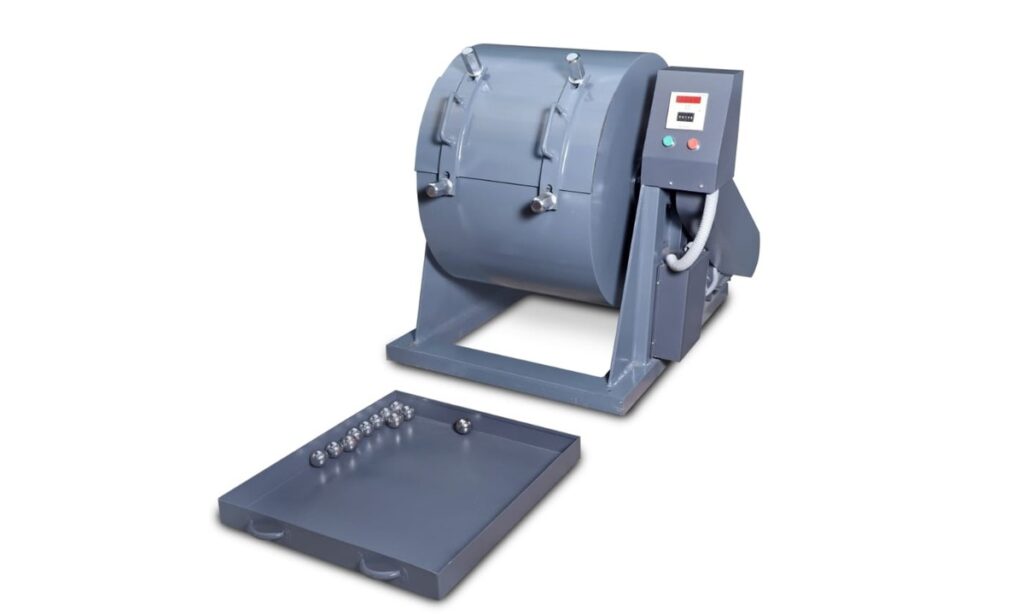

This is also known as Los Angeles Abrasion Test or L.A Abrasion test.
a) IS codes for Abrasion Aggregates Test:
- IS 2386(Part 4):1963
- BS 812–113:1990
b) Apparatus used for Abrasion Aggregates Test:
- Los Angeles Abrasion Machine
- Steel balls: 11no.
- Weighing machine
- Sieves: 20, 12.5, 10, 1.7mm
c) Procedure of Abrasion Test:
- Take clean, dry aggregate sample and place it in a Los Angeles Abrasion Testing Machine along with steel balls.
- Rotate the machine at a speed of 30 to 33 rpm (revolution per minute) for a set total of 500 to 1000 revolutions to subject the sample to abrasion and impact.
- After the designated number of revolutions, remove the sample and separate it into size fractions using a standard sieve of 1.7 mm.
- Weigh the material retained on the sieve and calculate the Los Angeles Abrasion Value (LAAV) as a percentage of the original sample weight.
d) Results Values: A maximum value of 35 percent is allowed for bituminous concrete and a value of 40 percent is allowed for the WBM base course.
3. Aggregate Impact Test
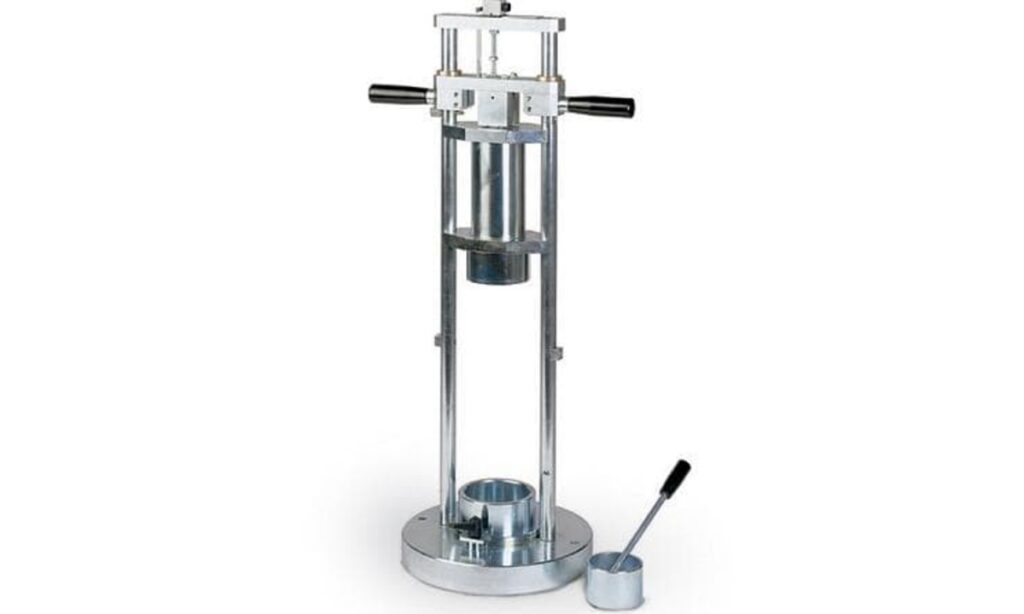

The impact test on aggregates, also known as the Aggregate Impact Value (AIV) test, is conducted to determine the aggregate’s resistance to sudden impacts or shocks. This test is essential for assessing the toughness or hardness of aggregates, particularly those used in road construction.
a) IS codes for Impact Test:
- IS 2386(Part 4):1963
b) Apparatus used for Impact Test:
- Aggregate impact apparatus
- IS sieves 12.5 mm, 10.0 mm, and 2.36 mm
- Cylindrical measure and Cylindrical Cup
- Weighing machine
- Tamping rod
c) Procedure of Impact Test:
- Take a sufficient aggregate sample(sieved through a 12.5mm sieve and retained on a 10mm sieve) and ensure it is clean and free from dust and other particles.
- Dry the sample in an oven at a specified temperature until it attains a constant weight.
- Place the dry aggregate sample in the impact testing machine.
- Apply a specified impact or 15 number of striking blows from a metal hammer uniformly on the aggregate sample.
- Measure the percentage of fines produced(W2) by the aggregate sample due to the impact, typically passing through a specified sieve size of 2.36mm.
d) Results Values: A maximum value of 35 percent is allowed for bituminous concrete and a value of 40 percent is allowed for the WBM base course. (Same as abrasion test results)
4. Soundness Test on Aggregates
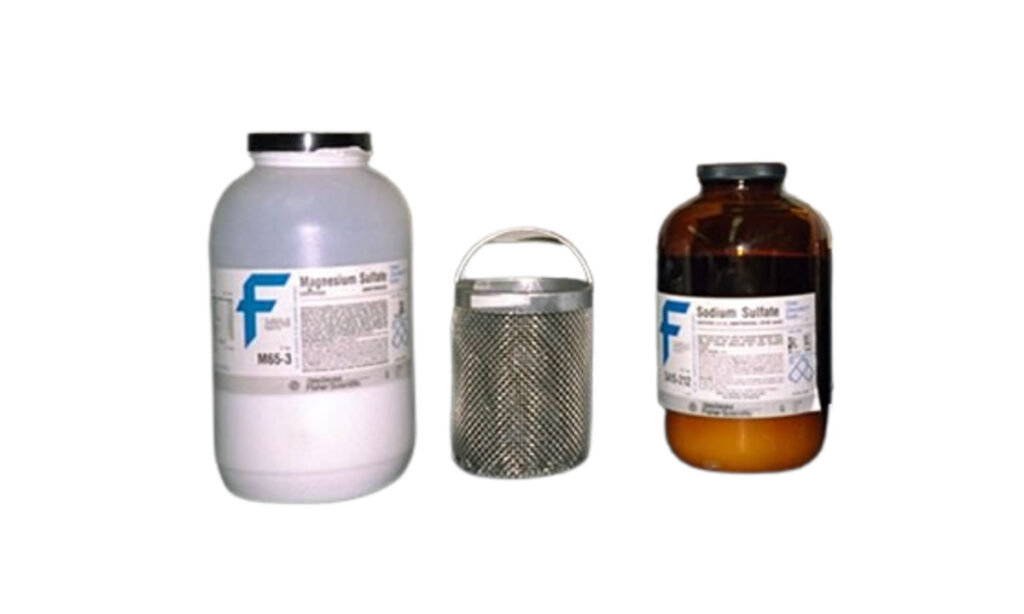

The soundness test on aggregates is conducted to determine the resistance of aggregates to disintegration or degradation caused by physical weathering or chemical action, particularly in concrete exposed to adverse environmental conditions.
a) IS codes for Soundness Test:
- IS 2386(Part 5):1963
- BS 812-121:1989
b) Apparatus used for Soundness Test:
- Sodium Sulphate or Magnesium Sulphate Solution
- Oven
- Weighing Machine
- IS Sieves
c) Procedure of Soundness Test:
- Take a clean and dust-free aggregate sample and weigh it.
- Immerse the dry sample in a saturated solution of sodium sulfate or magnesium sulfate for 16 to 18 hours.
- Now Drain the sample for 15 minutes and keep it in the oven for drying.
- Repeat the cycle as per requirements and examine the sample for signs of disintegration or surface deterioration.
- Compare the conditions before and after the test.
d) Results Values: The loss in sample weight should not exceed 12 percent when tested with sodium sulfate and 18 percent with magnesium sulfate solution.
5. Shape Test on Aggregates
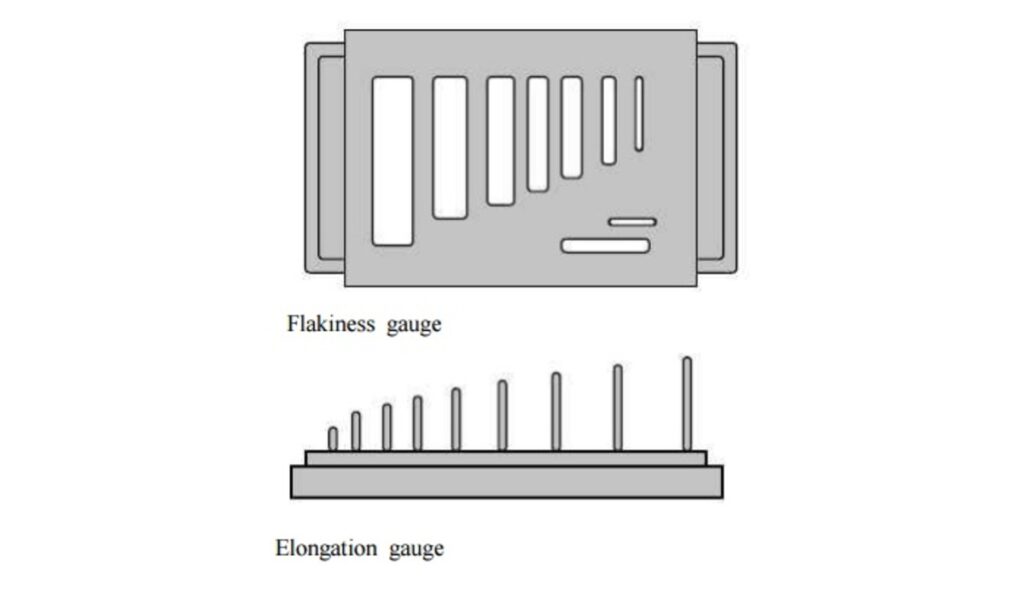
This aggregate test is carried out to determine the shape characteristics of coarse aggregates such as angularity and texture, which can impact the workability, strength, and durability of concrete.
Shape test on aggregates is also known as shape index test.
a) IS codes for Shape Test:
- IS 2386(Part 1):1963
- BS 812-105.1:1989
b) Apparatus used for Shape Test:
- Thickness gauge
- Length gauge
- Weighing machine
- IS Sieves
c) Procedure of Shape Test:
- Take sufficient coarse aggregate sample and ensure it is clean and free from dust, fines, and other contaminants.
- Dry the sample in an oven at a specified temperature until it attains a constant weight.
- Select a random portion of the dried aggregate sample and spread it evenly on a flat surface.
- Visually inspect and classify the particles into different shape categories such as cubical, elongated, flaky, or rounded, based on predefined criteria or standards.
- Count the number of particles falling into each shape category and record the observations.
d) Results Values: The result of the aggregate shape test should range between 15% to 30% based on the area of use.
6. Specific Gravity and Water Absorption Test on Aggregates
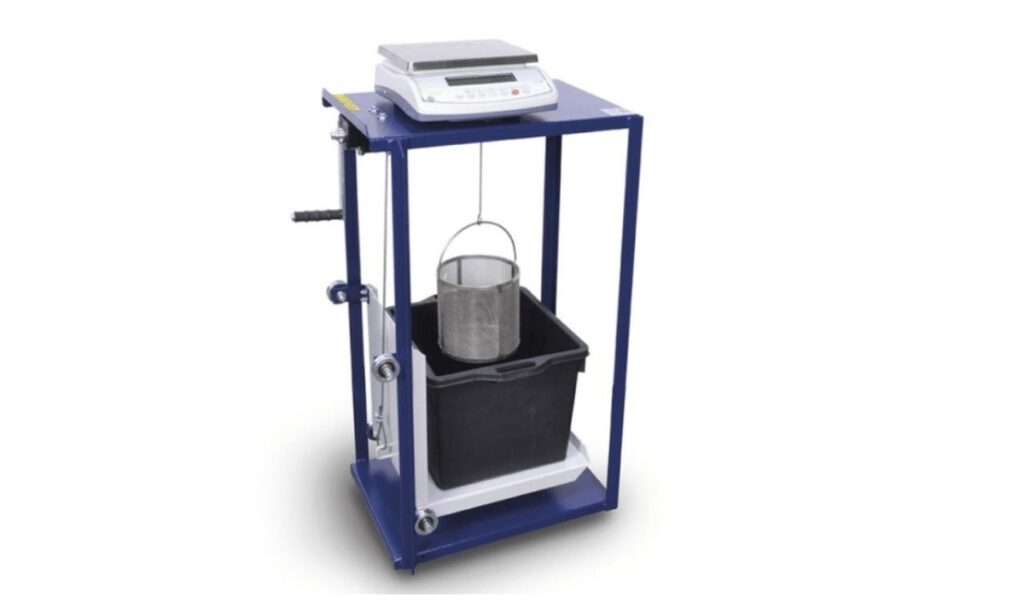

The specific gravity and water absorption test is conducted on aggregates to determine the density and water absorption characteristics. These properties helps in determining the quality and suitability of aggregates for use in concrete and other construction applications.
a) IS codes for Specific Gravity and Water Absorption Test:
- IS 2386(Part 3):1963
- BS 812-2:1995
b) Apparatus used for Specific Gravity and Water Absorption Test:
- Density basket
- Weighing machine
- Water tank
- Tray
- IS sieves- 10mm and 20mm
c) Procedure of Specific Gravity and Water Absorption Test:
- Collect a representative sample of coarse and/or fine aggregates and ensure it is clean and free from dust and other contaminants.
- Dry the sample in an oven at a specified temperature until it attains a constant weight.
- Weigh a clean, dry specific gravity bottle (Pycnometer) filled with distilled water (W1).
- Fill the specific gravity bottle with a known mass of dry aggregate (W2).
- Weigh the specific gravity bottle containing the aggregate and water (W3).
- Calculate the apparent specific gravity of the aggregate using the formula:
Specific Gravity= (W2 – W1)/(W3 – W1) - Repeat the procedure with a fresh sample to ensure accuracy.
Water absorption test
- Submerge the dry aggregate sample in water at room temperature for a specified duration (typically 24 hours).
- Remove the sample from the water, drain the excess water, and wipe the surface dry with a cloth.
- Weigh the saturated surface-dry (SSD) aggregate sample (W4).
- Calculate the water absorption of the aggregate using the formula:
Water Absorption = 100 (W4 – W2)/(W2) - Repeat the procedure with a fresh sample to ensure accuracy.
d) Results Values: The result value should range in between 2.5 to 3.0 for specfic gravity and water absorption should range from about 0.1 % to 2.0 %.
7. Bitumen Adhesion Test on Aggregates
This aggregate test is conducted to evaluate the ability of aggregates to adhere to bitumen in asphalt mixtures. This test helps in assessing the susceptibility of asphalt mixes to moisture damage and the effectiveness of adhesion between bitumen and aggregates.
The bitumen adhesion test on aggregates, is also known as the stripping test or bitumen-aggregate adhesion test.
a) IS codes for Bitumen Adhesion Test on Aggregates:
- IS:6241- 1971
b) Apparatus used for Bitumen Adhesion Test on Aggregates:
- Water Bath
- Oven
- Sieve
- Mixer to mix aggregate and bitumen
c) Procedure of Bitumen Adhesion Test on Aggregates:
- Take a sample of 200 gm dry aggregates passing a 20mm sieve and retained on a 12.5mm sieve.
- Heat the desired amount of bitumen to a specified temperature until it becomes fluid.
- Mix the dry aggregates with the heated bitumen using a mechanical mixer or other suitable equipment until the aggregates are fully coated with bitumen.
- Transfer the mixture into a 500ml cylindrical mold and allow it to cool at room temperature for approximately 2 hours.
- Add distilled water to the mold and immerse the coated aggregates.
- Cover the mold and place it in a water bath for 24 hours.
- Remove the mold from the water bath and let it cool at room temperature.
- Visually observe the uncovered area of the coated aggregates for any signs of stripping or loss of adhesion.
d) Results Values: The result value should not exceed 5%.

